
Want to shrink your mortgage payments in 2025 without feeling broke all month? Or maybe you’d love to pay off your home loan faster and save thousands in interest. If your mortgage feels like the bill everything else has to work around—from vacations to retirement savings—you’re not alone. In this guide, we’ll walk through the two big options, mortgage recast vs refinance, and show how each one fits into a bigger plan for your money, with a broader overview in our mortgage guide for homeowners.
It’s easy to feel overwhelmed by financial jargon, but understanding the difference between recasting your mortgage and refinancing it is crucial for making savvy money moves. This guide breaks down how each option works, what they cost, their benefits, and when each makes the most sense. Try the calculator below with your own numbers, then get ready to unlock real mortgage savings and take control of your financial future. ✨
This post contains affiliate links. If you buy through our links, we may earn a commission at no extra cost to you. Learn more.
Table of Contents
- Key Takeaways: Recasting vs Refinancing Your Mortgage
- Mortgage Recast vs Refinance Savings Calculator
- Why Your Mortgage Matters in 2025
- Mortgage Recast: Lower Payments with a Lump Sum
- Mortgage Refinance: A New Loan for New Goals
- Head-to-Head Comparison
- How to Decide
- Real-Life Scenarios (Examples)
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Your Path to Mortgage Savings
- How we put this guide together
Mortgage Recast vs Refinance Savings Calculator
Wondering what this might look like with your own mortgage? Adjust the sliders or type your numbers to compare a recast vs a refinance in the table below.
Your current loan
Recast option Lump sum
Refinance option
Your comparison
| Metric | Recast | Refinance |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Payment | $0.00 | $0.00 |
| Monthly Savings vs Now | $0.00 | $0.00 |
| Total Interest Saved | $0.00 | $0.00 |
| Payoff Time | — | — |
| Upfront Fees | $0.00 | $0.00 |
Calculator results are estimates for general planning only. Always confirm details and options with your lender or a qualified financial professional.
Key Takeaways: Recasting vs Refinancing Your Mortgage
- Mortgage Recast: Perfect if you’ve got a chunk of cash and want smaller monthly payments without messing with your interest rate or loan length. It’s usually cheaper and quicker than refinancing.
- Mortgage Refinance: Great for grabbing a lower interest rate, switching up your loan term, or pulling cash from your home’s equity. You’ll need a new loan, and it comes with closing costs.
- Cost & Credit Impact: Recasting keeps things simple with low fees and no hit to your credit. Refinancing has larger upfront costs and may cause a small, temporary credit dip.
- Mortgage Savings Goals: Recasting lowers your monthly payment; refinancing can slash total interest if rates are lower.
- When to Choose: Recast if you’ve got extra cash. Refinance if rates are lower, you want to change term or loan type, or need cash-out.
Why Your Mortgage Matters in 2025
Your mortgage is likely your biggest financial commitment, impacting your monthly budget, long-term wealth, and peace of mind. Actively managing it—through a mortgage recast or refinance—can lead to significant savings and more flexibility. If you’re also tightening the rest of your budget, our guide on how to live frugally and save money pairs well with mortgage moves like these.
In 2025, mortgage rates have been anything but calm, which makes each decision around your home loan feel higher stakes. Forecasts change often, so tools like Fannie Mae’s economic forecasts are useful for spotting trends, but you’ll still want to check up-to-date rates before you apply or lock anything in. When we talk with readers, the biggest turning point is realizing their mortgage isn’t set in stone—they can revisit it when jobs, families, or interest rates change.
If you’ve ever stared at your online banking wondering how to free up more room in your budget, that’s usually a sign it’s time to run the numbers. A simple first step is to log in to your loan account and jot down your current balance, interest rate, and remaining term so you know exactly what you’re working with.
Mortgage Recast: Lower Payments with a Lump Sum
Imagine you receive a significant cash windfall—perhaps a work bonus or an inheritance. You want your mortgage to feel more manageable. That’s where this decision comes in, and a recast often shines for simplicity. In plain English: if you’ve got a chunk of cash and you like your current interest rate, recasting is often the “don’t overthink it” option.
What is Recasting Your Mortgage?
A mortgage recast happens when your lender recalculates the monthly payment after a large lump-sum principal payment. Your original interest rate and term remain the same.
Example Scenario: The Windfall
Sarah has a $250,000 mortgage at 4.5% with 25 years left. She applies $50,000 to principal. After the recast, her payment drops, easing her budget.
How Does Mortgage Recasting Work?
- Make a Lump Sum Payment: Typically $5,000 or more.
- Request a Recast: Ask your lender to initiate it.
- Lender Recalculates: Payment adjusts based on the reduced principal.
- New Payment Begins: Starts with the next statement.
Eligibility for Mortgage Recasting
- A sizable lump-sum payment applied to principal.
- Conventional loans are commonly eligible; FHA/VA/USDA generally are not.
- Your lender must offer recasting.
Costs of Recasting
Fees for a mortgage recast often range from $150–$500. Some lenders even waive them, which is why a recast is usually a low-cost way to lower payments compared to a full refinance. If you like to see the math, plug your own balance and extra payment into our free mortgage payoff calculator to see how a lump sum could change your payoff timeline. Before you send a large extra payment, also check whether your loan has any prepayment penalties, since those could reduce or offset the benefit.
Pros and Cons of Mortgage Recasting
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low fees. | Requires a large lump sum. |
| Credit Impact | No credit check. | Interest rate unchanged. |
| Process | Quick, minimal paperwork. | Doesn’t shorten term unless you keep paying extra. |
| Eligibility | Common on conventional loans. | Often unavailable for FHA/VA/USDA. |
| Outcome | Lower monthly payment. | Less total interest savings vs a lower-rate refi. |
Think of recasting as pressing “reset” on your payment amount—without changing your rate or term.
After you’ve read through this section, a quick next step is to call or message your loan servicer and ask whether they offer recasts, what minimum lump sum they require, and what their recast fee looks like.
Mortgage Refinance: A New Loan for New Goals
Refinancing lets you swap your current mortgage for a new one. It can lower your rate, change your term, or unlock equity through cash-out.
What is Refinancing Your Mortgage?
In practice, that means you take out a new loan to pay off the old one. Examples include switching from an ARM to a fixed-rate loan for stability, or moving from 30 years to 15 years to pay off faster.
Example Scenario: Rate Drop
Mark has a $300,000 mortgage at 6%. Rates drop to 4%, so refinancing lowers his monthly payment and total interest (even after fees).
How Does Refinancing Work?
- Shop Lenders: Compare rates and terms.
- Apply: Submit financial documents.
- Credit & Appraisal: Lender checks credit and home value.
- Underwriting: Application review.
- Closing: Sign, pay fees, start the new loan.
Depending on your lender, this can feel a lot like getting your original mortgage again—expect paperwork, follow-up questions, and a few weeks of back-and-forth.
Eligibility for Refinancing
- Solid credit (e.g., 620+ for conventional loans).
- Stable income and manageable debt-to-income ratio.
- Having around 20% equity (an 80% loan-to-value ratio) helps you avoid PMI and may unlock better refinance terms.
Costs of Refinancing
For a mortgage refinance, expect 2–5% of the loan amount in closing costs (origination, appraisal, title, and more). That 2–5% range is a common guideline you’ll see from lenders and consumer finance resources, but your exact numbers will come from your Loan Estimate. When we run sample refinance scenarios in calculators, closing costs are usually what make or break the decision. Sometimes those costs can be rolled into the new loan, but it’s still smart to compare them with your projected monthly savings to find your break-even point. Our mortgage refinance break-even calculator can help you estimate how long it might take to earn that money back.
Since refinancing often means revisiting your whole housing budget, it can also be a smart time to compare home insurance quotes.
Pros and Cons of Mortgage Refinancing
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Rate/Term | Potentially lower rate or term change. | Extending term can raise lifetime interest. |
| Cash-out | Access to equity at mortgage rates. | Higher balance increases interest paid. |
| Process | Can restructure your loan completely. | More paperwork; longer timeline. |
| Credit | Long-term improvement possible. | Hard inquiry may cause a brief dip. |
| Costs | May pay for itself over time. | 2–5% closing costs upfront. |
Refinancing is a marathon: upfront costs, long-term payoff. Calculate your break-even and plan to stay put long enough.
If refinancing sounds promising, block off 30–60 minutes this week to request quotes from at least two lenders so you can compare their rates, fees, and total costs side by side.
Mortgage Recast vs Refinance: Head-to-Head Comparison
Here’s a side-by-side to see which option fits your situation.
| Feature | Mortgage Recast | Mortgage Refinance |
|---|---|---|
| What it is | Recalculates payment after a lump sum. | Replaces old loan with a new one. |
| Lump Sum? | Yes (e.g., $5,000+). | No lump sum required. |
| Rate Change? | No. | Yes (often lower). |
| Term Change? | No. | Yes (flexible). |
| Fees | Low admin fee. | 2–5% closing costs. |
| Credit Check? | No. | Yes (hard pull). |
| Goal | Lower monthly payment. | Lower rate, new term, or cash-out. |
As you scan this comparison, highlight the 1–2 rows that matter most to you—like fees, credit checks, or flexibility—and use those as your main tie-breakers between a recast and a refinance.
Deciding Between Recasting and Refinancing Your Mortgage
Still torn between the two? Start with your goals and rate environment. Recast for immediate payment relief when you have a lump sum; refinance when market rates are noticeably lower or you need to change your term or loan type.
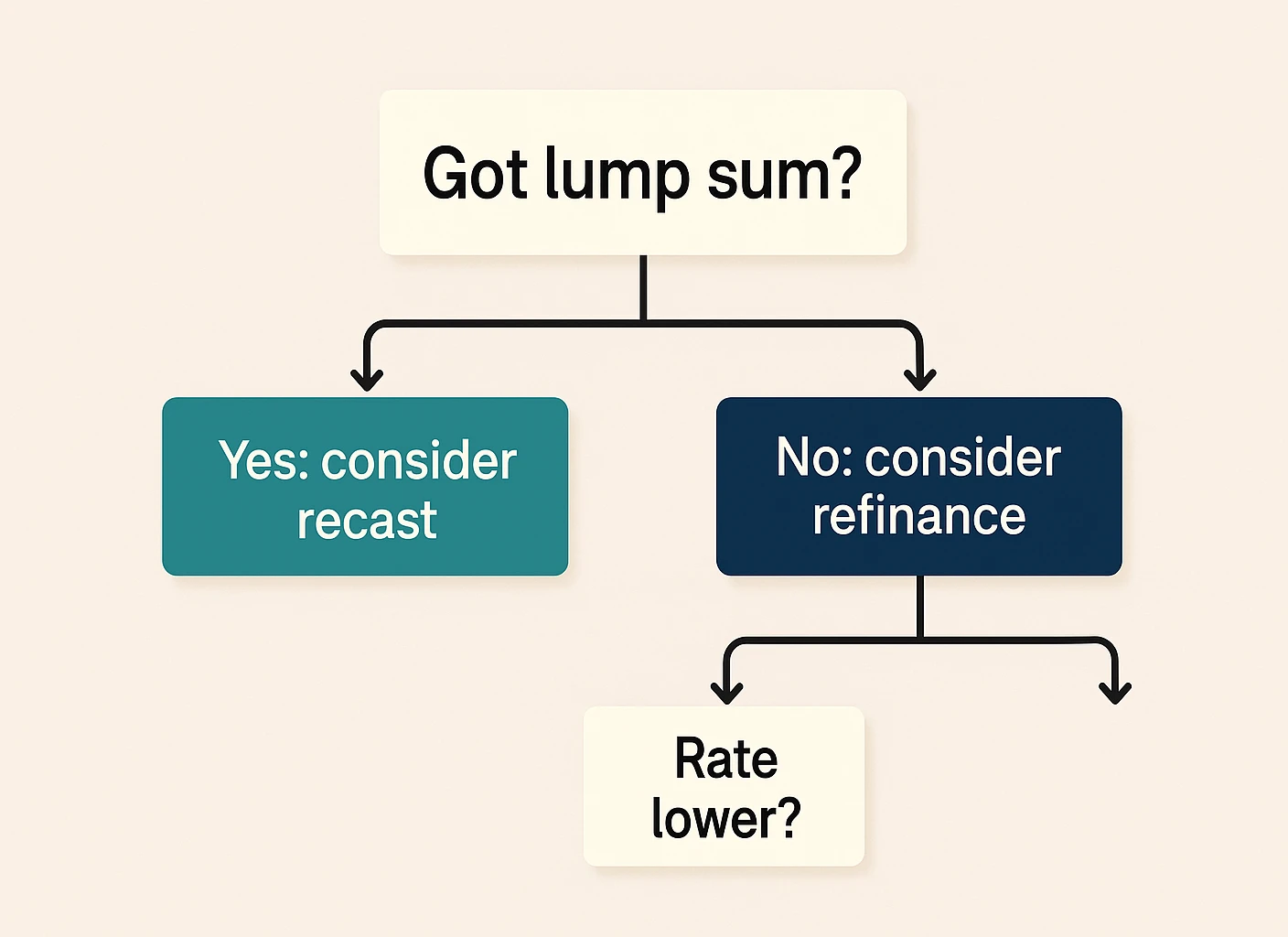
Key Questions to Ask
- What’s my primary goal—payment relief, interest savings, or cash-out?
- Do I have a lump sum for a recast?
- How do current rates compare to mine?
- How long will I stay in this home?
- Is my loan eligible for recasting?
When neither recast nor refinance is a great idea
- You’re likely to sell or move within the next few years, so there’s not enough time to earn back closing costs.
- Your income or job situation is unstable and you may need maximum flexibility with your cash.
- You’re juggling high-interest debt, and every extra dollar may work harder paying that down first.
If these points sound familiar, your next move might be to pause and focus on stabilizing your income, paying down higher-interest debt, or building a small emergency fund before you change your mortgage.
If you’re still unsure after that, write down your top one or two money goals and ask a lender or financial professional to show you how a recast and a refinance would change your monthly payment and total interest.
Real-Life Scenarios (Examples)
Three quick stories to show how real people might use a recast or refinance. See which one feels closest to your situation—that’s usually the best clue about whether recasting or refinancing fits you better.
Scenario A: Cash Windfall (Recast)
Who: David, a teacher
His Deal: Owes $350,000 at 4.8% with 28 years left (≈$1,830/mo).
What Happened: Inherits $75,000 and wants budget relief.
Choice: Recast to $275,000; payment drops by ≈$400/month. Low fee, minimal hassle.
Scenario B: Rate Drop (Refinance)
Who: Emily, business owner
Her Deal: $400,000 at 6.5% for 20 years (≈$2,970/mo).
What Happened: Rates at ~4% and she’ll stay 10+ years.
Choice: Refinance to ~4%; payment ≈$2,420. $8,000 costs recoup in ~16 months.
Scenario C: Cash-Out Refinance
Who: Frank, DIYer
His Deal: $200,000 at 4.2% with 18 years left; home worth $350,000.
What Happened: Needs $50,000 for reno + debt consolidation.
Choice: Cash-out refi to $250,000 at ~4.5%, payments still manageable.
Frequently Asked Questions
If these FAQs spark new questions, jot them down and bring them to a call or email with your lender so you can walk away with clear, written answers.
Your Path to Mortgage Savings
Now that you know the trade-offs between recasting and refinancing your mortgage, use the calculator to model your numbers, then talk to your lender about eligibility, fees, and timing. You can also explore biweekly mortgage payments as another way to chip away at interest without a full recast or refi. Small decisions you make this year can free up your cash flow and meaningfully cut total interest over time.
The homeowners we hear from who feel most confident afterward are usually the ones who spend an hour or so running a few scenarios and asking “what if” questions before they commit.
What to do next
- Get today’s refinance quotes from 2–3 lenders so you can compare real rates and closing costs.
- Ask your current servicer if they allow recasts, what the minimum lump sum is, and what their recast fee looks like.
- Plug your actual numbers into this calculator and the refinance break-even tool to see how each path plays out.
- Decide what matters more right now: a lower monthly payment for breathing room or the lowest possible total interest over the life of the loan.
How we put this guide together
- We cross-checked typical recast and refinance fees, eligibility rules, and break-even ranges against major lenders and public mortgage resources.
- All examples use realistic but rounded numbers so you can quickly compare them to your own loan without getting lost in decimals.
- The calculators and scenarios are educational tools only—your lender’s actual terms, timelines, and costs may differ, so always confirm before making a final decision.
If you like to double-check numbers, you can also ask your lender for an amortization schedule or payment breakdown so you can compare it with the examples and calculators in this guide.
This guide is for general information and education only and isn’t financial, legal, or tax advice. It doesn’t take into account your full situation, and individual results will always vary. Before changing your mortgage, payments, or broader financial plan, talk with a qualified professional who can review your personal details.

